PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
6.0 - 7.6
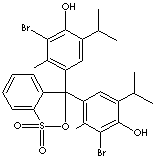
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
Bromothymol Blue (BTB) is a pH indicator (pKa approx. 7.1) that is used as a
biological slide vital stain to define cell walls or nuclei under the
microscope. BTB is also a component of several bacterial growth and detection
substrates such as cystine lactose electrolyte deficient (CLED/BROLACIN);
polymyxin pyruvate egg yolk mannitol bromothymol blue (PEMBA) and MacConkey
agar.
Local: The relationship between the activity of hydrogen ions [exactly hydronium ions, H(H2O)n+] and concentration of a solution is fundamentally important to determine the extent of a chemical reaction, as it affects the equilibria and kinetics of a wide variety of chemical and biochemical reactions. The hydrogen-ion activity refers to the effective concentration of unassociated hydrogen ions, the form that directly affects physicochemical reaction rates and equilibria. The symbol, pH, numerically relates the hydrogen ions concentration or activity. The pH is approximately equal to the negative logarithm of H+ concentration expressed in molarity. pH 7 is neutral; above it alkalinity increases and below it acidity increases. pH indicators are usually weak acidic or basic organic tautomers which exist in more than one structural form of which at least one form is characteristically colored in relation to different electronic configuration of the bound. Indicators should not change color exactly at one pH value, but within a wide pH range. The transition point of an indicator is defined as the point at which the acid and alkaline forms of the indicator exist in equal concentrations. Visual transition intervals are as below:
- alpha-Naphthol phthalein (CAS #: 596-01-0): from pH 7.3 (pinkish-yellow) to pH 8.7 (greenish-blue)
- Bromocresol green (CAS #: 76-60-8): from pH 3.8 (yellow) to pH 5.4 (blue)
- Bromcresol Purple (CAS #: 115-40-2): from pH 5.2 (yellow) to pH 6.8 (purple)
- Bromochlorophenol Blue (CAS #: 2553-71-1): from pH 3.2 (yellow) to pH 4.8 (blue)
- Bromocresol purple, sodium salt (CAS #: 62625-30-3): from pH 5.2 (yellow) to pH 6.8 (purple)
- Bromophenol blue (CAS #: 115-39-9): from pH 3.0 (yellow) to pH 4.6 (blue)
- Bromophenol blue, sodium salt (CAS #: 62625-28-9): from pH 3.0 (yellow) to pH 4.6 (blue)
- Bromopyrogallol Red (CAS #: 16574-43-9): suitable for complexometric or chelometric titrations
- Bromothymol blue (CAS #: 76-59-5): from pH 6.0 (yellow) to pH 7.6 (blue)
- Bromothymol blue, sodium salt (CAS #: 34722-90-2): from pH 6.0 (yellow) to pH 7.6 (blue)
- Bromoxylenol Blue (CAS #: 40070-59-5): from pH 6.0 (yellow) to pH 7.6 (blue)
- Chlorophenol Red, water soluble (CAS #: 123333-64-2): from pH 4.6 (yellow) to pH 7.0 (purple)
- Cresol Red (CAS #: 1733-12-6): from pH 7.0 (orange) to pH 8.8 (purple)
- Fluorescein (CAS #: 2321-07-5)
- Fluorescein sodium (CAS #: 518-47-8):
- Glycinethymol Blue (CAS #: 3810-63-7):
- Iodophthalein sodium (CAS #: 2217-44-9)
- m-Cresol purple (CAS #: 2303-01-7): from pH 7.4 (yellow) to pH 9.0 (purple)
- Methylthymol blue, sodium salt (CAS #: 1945-77-3): suitable for complexometric or chelometric titrations
- o-Cresolphthalein (CAS #: 596-27-0): from pH 8.2 (colorless) to pH 9.8 (red)
- o-Cresolphthalein Complexone (CAS #: 2411-89-4): suitable for complexometric or chelometric titrations
- Phenolphthalein Complexone (CAS #: 25296-54-2):
- Phenol Red (CAS #: 143-74-8): from pH 6.8 (yellow) to pH 8.2 (red)
- Phenol Red Sodium Salt (CAS #: 34487-61-1): from pH 6.8 (yellow) to pH 8.2 (red)
- Phenolphthalein (CAS #: 77-09-8): from pH 8.5 (colorless) to 9.0 (red)
- p-Xylenol Blue (CAS #: 125-31-5):
- Acid range: from pH 1.2 (red) to pH 2.8 (yellow)
- Alkali range: from pH 8.0 (yellow) to pH 9.6 (purplish-blue)
- Pyrocatechol violet (CAS #: 115-41-3): suitable for determination of many metals (complexometric or chelometric titrations) particularly rapid for tin
- Pyrogallol Red (CAS #: 32638-88-3):
- Thymol Blue, sodium salt (CAS #: 62625-21-2):
- Acid range: from pH 1.2 (red) to pH 2.8 (yellow)
- Alkaline range: from pH 8.0 (yellow) to pH 9.2 (blue)
- Thymolphthalein Complexone (CAS #: 1913-93-5): suitable for complexometric or chelometric titrations
- Thymolphthalein (CAS #: 125-20-2): from pH 8.8 (colourless) to pH 10.5 (blue)
APPEARANCE
DYE CONTENT
~ 95.0%
SOLUTION CLARITY
Pass